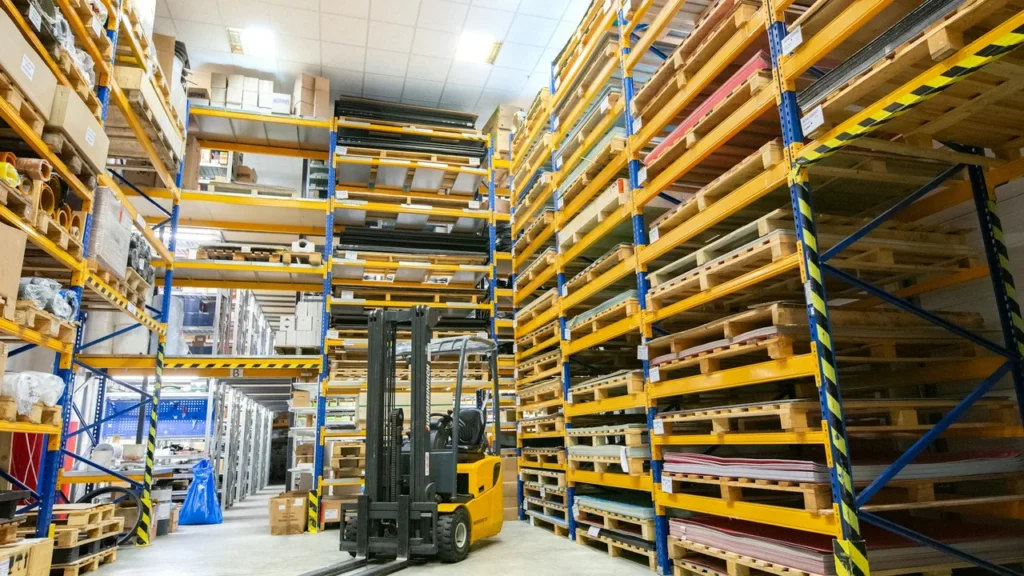
In today’s fast-paced industrial landscape, the steel structure warehouse stands as a symbol of progress and practicality. As businesses expand globally and supply chains become increasingly complex, the need for durable, efficient, and adaptable warehouse solutions has never been greater. Modern warehouse design now integrates cutting-edge materials, digital management systems, and sustainability principles—all while prioritizing large-span construction to maximize usable space and operational flow.
The Role of Warehouses in Modern Industry
Warehouses are no longer simple storage buildings; they have evolved into high-performance facilities central to manufacturing, distribution, and e-commerce. These facilities form the core of logistics centers that keep products moving from factories to markets. As the global economy leans toward speed, precision, and automation, warehouse infrastructure must evolve to support modern industrial demands.
Evolution of Warehouse Design
The concept of a warehouse has changed dramatically over the decades. Early designs focused solely on storage volume, with minimal attention to process efficiency. Today, warehouses are designed as operational ecosystems—integrating automation, smart sensors, and structural engineering for flexibility and scalability. The best warehouse design prioritizes material handling efficiency, vertical space utilization, and adaptability to future technologies such as robotics and automated guided vehicles (AGVs).
Why Choose Steel Structure for Warehouses
The shift from traditional concrete or brick buildings to steel structure warehouses has redefined industrial construction. Steel has emerged as the preferred material for large-span facilities due to its combination of strength, speed, and sustainability. Unlike conventional structures, a steel warehouse can support clear spans exceeding 100 meters, enabling unobstructed internal layouts ideal for high-density storage and automated systems.
Advantages of Steel Structure Warehouse Construction
- Exceptional Strength and Durability: Steel provides outstanding load-bearing capacity, withstanding heavy machinery, overhead cranes, and environmental stress.
- Speed and Cost Efficiency: Prefabrication allows for rapid assembly, reducing on-site labor costs and construction time significantly.
- Design Flexibility: From small logistics centers to massive cold storage facilities, steel structures can adapt to different industries with ease.
- Long-Term Sustainability: Steel components are 100% recyclable, aligning with green building standards and circular economy principles.
Comparing Steel vs. Traditional Materials
| Feature | Steel Structure Warehouse | Concrete / Brick Building |
|---|---|---|
| Span Length | Up to 100m+ without interior columns | Limited to short spans |
| Construction Time | Fast assembly using prefabricated frames | Slow curing and longer completion time |
| Weight | Lightweight, reduces foundation cost | Heavy, requires deeper foundations |
| Maintenance | Easy inspection and modular replacement | Frequent repairs, high material costs |
Key Design Principles for Large-Span Warehouses
Designing a large-span steel structure warehouse demands precise engineering and careful planning. Every element—from the frame geometry to the layout of loading bays—affects the building’s efficiency, durability, and long-term cost performance. The ideal warehouse design must achieve a balance between structural integrity and functional workflow.
Structural Design Considerations
The structural system of a warehouse determines its overall performance. Large-span warehouses typically use portal rigid frames, space trusses, or lattice girders to achieve column-free interiors. Load-bearing calculations must account for live loads, snow accumulation, wind resistance, and seismic activity. The roof system is especially critical; lightweight purlins and high-strength cladding improve energy efficiency while reducing dead load. According to SteelConstruction.info, optimizing the spacing and section size of frames can reduce steel usage by up to 15% without compromising stability.
Space Planning and Functional Layout
Space utilization is the heart of efficient warehouse design. The interior should be planned for seamless material flow—covering receiving docks, storage zones, packing areas, and dispatch bays. A well-designed steel structure warehouse allows for the integration of mezzanine levels or automated racking systems, maximizing cubic storage capacity. Additionally, clear circulation paths for forklifts and automated vehicles reduce operational bottlenecks and enhance safety.
Integration of Technology
Modern industrial efficiency depends heavily on the integration of smart systems. Automated conveyors, RFID tracking, and warehouse management software (WMS) now operate within the architectural framework. To support these technologies, steel structures offer easy routing for electrical and data conduits. High-bay LED lighting, fire suppression systems, and energy-efficient insulation further improve operational performance and sustainability.
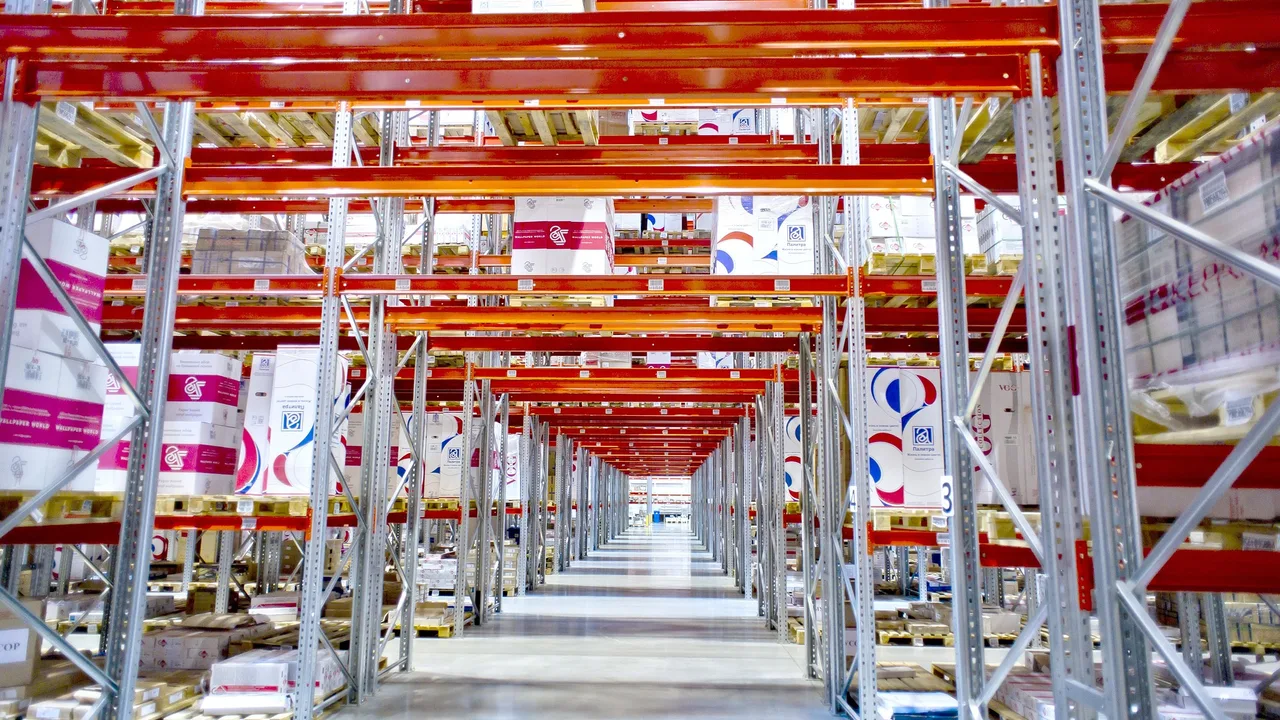

Construction Process of a Steel Structure Warehouse
The development of a steel structure warehouse involves a sequence of coordinated steps that ensure quality, accuracy, and on-time delivery. From conceptual design to final inspection, every stage leverages precision engineering and prefabrication techniques to achieve optimal results.
From Design to Completion
The process begins with feasibility studies and preliminary design, followed by detailed engineering based on site conditions and functional requirements. Engineers use advanced software and Building Information Modeling (BIM) to simulate load paths, detect conflicts, and visualize the project in 3D. BIM-driven collaboration minimizes errors and accelerates decision-making, ensuring that fabrication aligns perfectly with on-site conditions.
Once designs are approved, steel components are fabricated in controlled factory environments. Prefabrication guarantees dimensional accuracy and reduces material waste. The fabricated elements—columns, beams, and roof trusses—are then transported to the site for assembly using cranes and bolted connections. With proper project scheduling, even large-scale warehouses can be erected within weeks rather than months.
Fabrication and Erection of Steel Structure Warehouses
The fabrication and erection phase defines the quality and longevity of a steel structure warehouse. Each steel component—columns, rafters, trusses, and bracings—is pre-engineered to meet precise design loads. Modern fabrication lines use CNC plasma cutting, automatic welding, and corrosion-resistant coatings to ensure durability and precision.
During erection, bolted and welded joints are assembled following strict safety and alignment protocols. Cranes lift major structural members into position, while skilled crews secure connections with calibrated torque tools. Because most components are prefabricated, on-site activities focus mainly on assembly, minimizing noise, waste, and weather-related delays. The modular nature of steel allows for easy future expansion, a major advantage for growing logistics centers.
Safety and Quality Control
Quality assurance begins at the manufacturing stage and continues throughout installation. Ultrasonic and magnetic particle tests verify weld integrity, while dimensional checks ensure perfect alignment. Erection crews follow occupational safety standards, using harnesses, guardrails, and lift platforms to reduce accident risk. A comprehensive quality checklist guarantees that each warehouse design meets both local building codes and international steel standards such as ASTM and EN1090.
Case Studies of Large-Span Steel Warehouses
Successful implementations around the world highlight the flexibility and reliability of steel structure warehouse solutions. These case studies show how engineering precision and optimized warehouse design enhance operational performance.
1. Automated Logistics Hub – Europe
This 80-meter-span distribution facility integrates high-bay storage, robotic picking systems, and temperature-controlled zones. The building’s steel frame supports over 30 meters of clear height, allowing automated cranes to operate without obstructions. Prefabricated portal frames and insulated sandwich panels reduce energy loss and maintain internal temperature stability.
2. Manufacturing Warehouse – Asia
Located in an industrial park, this facility required large open floors to accommodate heavy machinery and overhead cranes. Engineers selected a lattice-truss steel structure warehouse for superior rigidity and vibration resistance. The result was a 20% reduction in foundation cost and a 40% improvement in construction speed compared to concrete alternatives.
3. Cold Storage and Distribution Center – Middle East
For perishable goods, thermal performance is critical. This warehouse uses double-layer insulated roofing and reflective coatings to maintain internal temperatures below -20°C. The lightweight steel roof system minimizes load while accommodating integrated refrigeration ducts and photovoltaic panels that power auxiliary systems.
Performance Outcomes
- Reduced maintenance and operating costs through corrosion-protected steel frames.
- Improved logistics flow due to unobstructed large spans.
- Energy savings from insulated cladding and efficient ventilation systems.
Sustainability and Future Trends
Modern industrial construction emphasizes both efficiency and environmental responsibility. A steel structure warehouse aligns naturally with green-building goals thanks to its recyclability and adaptability. Steel can be melted and reused indefinitely without loss of strength, reducing waste generation across a project’s life cycle.
Green and Sustainable Warehouse Design
New generation warehouses integrate sustainable features such as:
- Solar Roofing Systems: Photovoltaic panels installed on large roof surfaces generate renewable energy for lighting and HVAC operations.
- Rainwater Harvesting: Gutter systems channel runoff into storage tanks for non-potable uses like cleaning and landscaping.
- Natural Ventilation and Lighting: Ridge vents, skylights, and translucent panels reduce dependency on artificial systems.
- Low-VOC Materials: Protective coatings and paints that minimize harmful emissions.
According to the BuildingSMART Alliance, digital twin modeling combined with sustainable material tracking can reduce a building’s embodied carbon by up to 30%. This makes sustainability not just an environmental goal but also an operational advantage for developers and tenants.
The Future of Logistics Centers
The next generation of logistics centers will merge architecture, automation, and data analytics. Smart warehouses will use sensors and AI to monitor temperature, humidity, and equipment performance in real time. Predictive maintenance systems will automatically alert operators to structural or mechanical issues before downtime occurs.
Furthermore, the integration of 5G and IoT technologies will allow seamless communication between forklifts, conveyors, and central control systems. Modular steel structure warehouses are ideally suited for this future—they can be reconfigured easily to support new technologies without major structural changes.
Economic Impact and Industrial Efficiency
Investing in a steel structure warehouse yields long-term economic benefits. The rapid construction cycle enables faster project turnover, while the low maintenance costs enhance return on investment. In industrial zones where land value is high, maximizing internal volume with large-span designs directly increases operational capacity per square meter.
For logistics centers that manage high throughput, the ability to reconfigure internal layouts quickly provides a competitive advantage. As e-commerce and global trade continue to expand, companies that adopt efficient warehouse design will outperform those constrained by older, inflexible facilities.
Conclusion
The evolution of the steel structure warehouse reflects the broader transformation of modern industry—toward speed, flexibility, and sustainability. Large-span steel systems deliver unmatched efficiency, enabling businesses to optimize workflows and adapt to changing market demands. By integrating smart technology, green materials, and precision engineering, the warehouse design of the future becomes more than just a building; it becomes a strategic asset.
As global industries move forward, adopting advanced steel structure warehouses ensures that production, storage, and distribution remain resilient, cost-effective, and environmentally responsible.